Can be a amplifier or a switch, but today let’s put notes about switches because i founded more interesting:
Silicon is a semiconductor
- 4 valence electrons
- Tetrahidro Cristal
Doping semiconductor n-type doping:
- injecting small amount of an element like Phosphorous, that is similar to silicon and have 5 valence electrons, and having one more than silicon make the conductivity better
- The negative electrons that moves p-type
- element with 3 valence electron like Boron that way it create a hole that also increase the conductivity because the electrons can move into the hole itself
- The hole that is a lack of electron make it actually acts like a positive charge and that’s why the “P” type, and the movement here is the holes itself By the way that doesn’t mean they are actually positive and negative but neutral because the electron number of electron and protons inside
Transistor are made of P-Type and N-Type doping
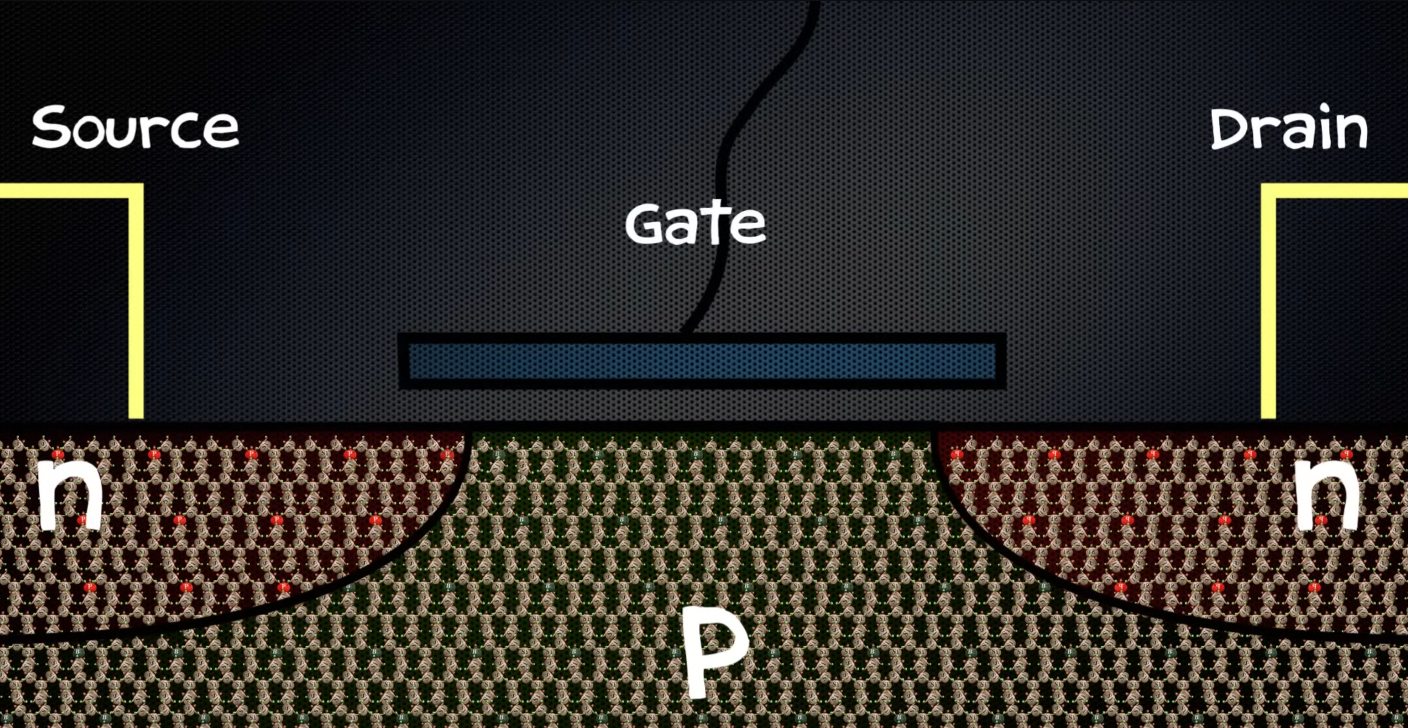
Electron contacts in the ends/edges, there is the electrical contact in the middle isolated by an oxide layer(the gate)
In the area between P and N, the N-type electron moves to the P type and creates something called depleted area, there is no free electrons in the n-type because they filled the P’s holes
- This makes the P-type repel electron that try to come across from the N-type, acting like a barrier This depleted area prevent the electron flow through the transistor, so the transistor state is off, it’s like a open switch (the zero state)
To turn it on needs a small positive voltage to the gate, attracting the electron through the gate making them form a conducting channel
- It makes the transistor on in the one state Continuation in logic gates